Time: 2025-03-11 13:43:35 Source: Henan Province Jianyun Cable Co., Ltd.
With the continuous expansion of offshore oil and gas exploration, umbilical cables have become critical components in underwater production systems. These cables serve as lifelines, providing power, communication, and hydraulic control to subsea equipment. However, the complex marine environment, including high pressures, dynamic loads, and chemical exposure, makes the reliability of umbilical cables a significant concern.
To ensure long-term performance and safety, full-scale testing is conducted under various operational conditions. This article explores the full-scale testing methods, the mechanical and electrical performance evaluations, and the impact of different environmental conditions on umbilical cables.
To comprehensively evaluate umbilical cables, a series of tests are conducted based on API SPEC 17E-2017 and CIGRE TB 862-2022 standards. These tests are divided into two categories: Verification Tests and Performance Tests.
Verification tests assess whether the design and manufacturing meet operational requirements.
| Test | Purpose | Key Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Cable Laying Test | Ensures proper cable formation and compactness | Outer diameter, twist pitch |
| Terminal Strength Test | Evaluates anchor point strength during deployment | Maximum tension load |
| Tensile-Bending Combination Test | Simulates tension and bending forces during installation | Bending radius, tensile load |
| Crush Test | Determines resistance to compression forces | Load pressure, deformation |
| Impact Test | Measures resistance to falling objects (rocks, anchors) | Impact energy (J) |
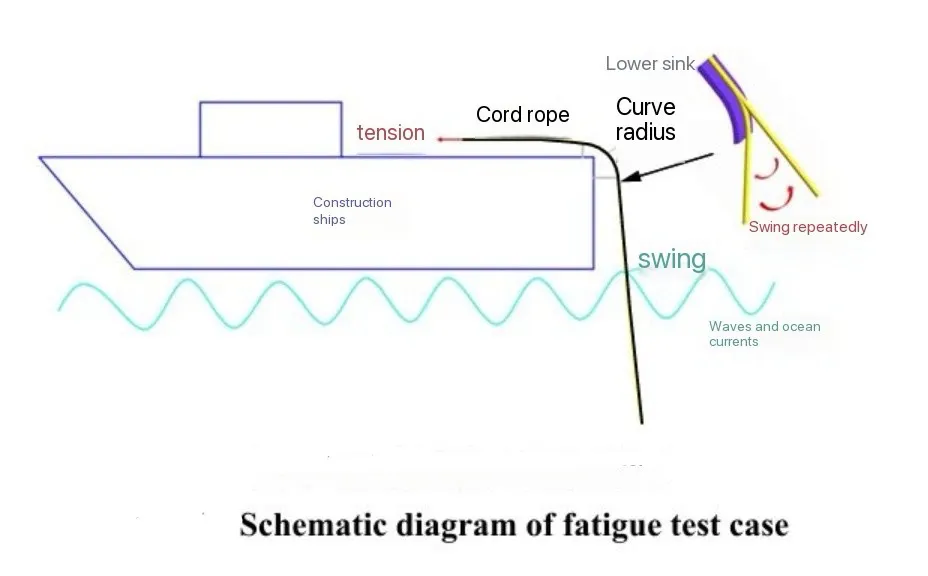
| Fatigue Test | Assesses long-term durability under cyclic loading | Number of cycles, applied stress |
| Hydrostatic Pressure Test | Tests resistance to deep-sea pressure | Water depth simulation |
| Topside Termination Interface Test | Verifies connection strength between umbilical and platform | Interface tension, pull-out force |
| Axial Compression Test | Evaluates behavior under vertical loading conditions | Axial load, deformation |
➡ Key Findings:
Performance tests quantify the electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties of umbilical cables.
| Test | Purpose | Measured Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile-Torsion Balance Test | Evaluates cable stretch and twist behavior | Axial stiffness, torsional balance |
| Bending Stiffness Test | Determines the minimum bending radius | Bending moment, stiffness coefficient |
| Internal & External Friction Test | Measures friction forces affecting installation | Friction coefficient |
| Free-Flooding Rate Test | Assesses water ingress behavior during installation | Flow rate, pressure differential |
| Tensioner Slip Test | Ensures secure clamping during cable laying | Slip resistance force |
| Temperature Rise Test | Evaluates heat dissipation in power-transmitting umbilicals | Conductor temperature, insulation performance |
➡ Key Findings:
As depth increases, cables experience greater hydrostatic pressure, affecting their structural integrity.
| Water Depth (m) | External Pressure (MPa) | Risk Factor |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 5.0 | Low |
| 1000 | 10.0 | Moderate |
| 2000 | 20.0 | High |
| 3000+ | 30.0+ | Extreme |
➡ Design Consideration: High-strength materials and multi-layer armor protection are needed for deep-sea applications.
During deployment and operation, umbilicals undergo tension and bending forces.
| Bending Radius (m) | Tensile Load (kN) | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 50 | Moderate |
| 3 | 75 | High |
| 2 | 100 | Critical |
➡ Finding: Larger bending radii reduce stress, preventing structural fatigue.
Full-scale testing is essential for ensuring the reliability and performance of umbilical cables in underwater production systems. By conducting verification and performance tests, engineers can:
✔ Identify potential failure points before deployment.
✔ Optimize cable design for deep-sea environments.
✔ Ensure long-term operational stability in dynamic offshore conditions.
With advancements in material technology and monitoring systems, umbilical cables will continue to play a pivotal role in offshore energy infrastructure.