Time: 2025-04-03 08:20:43 Source: Henan Province Jianyun Cable Co., Ltd.
Ground current monitoring, traction power system, railway electrification, real-time monitoring, fault detection, electrical safety, online monitoring technology.
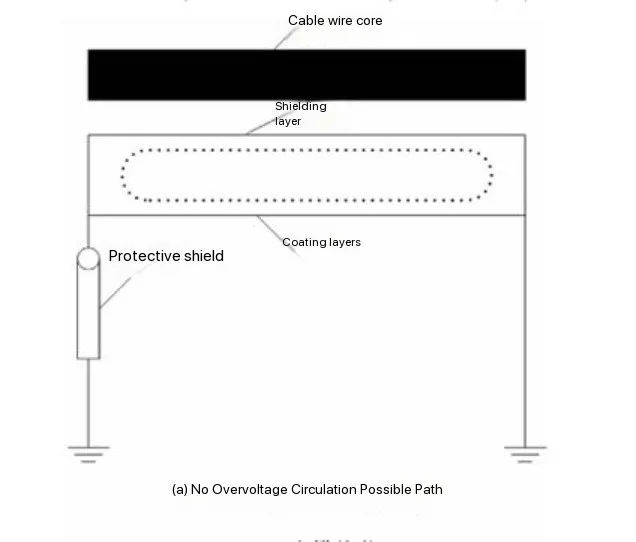
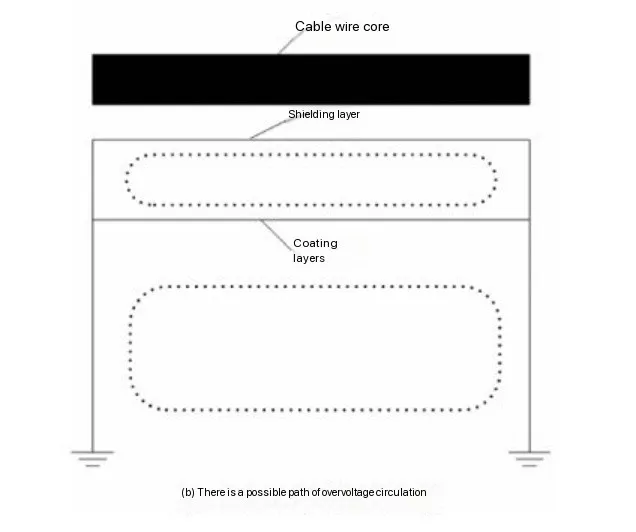
Modern railway electrification systems rely on efficient and safe power transmission to ensure seamless train operations. One of the critical challenges in traction power supply is the monitoring and control of ground currents, which can impact system performance and safety. Traditional monitoring methods often involve periodic manual inspections, which can lead to delays in fault detection and increased maintenance costs.
A recent study titled "Application of Online Ground Current Monitoring in Traction Power Cable Lines" explores an innovative real-time monitoring system to improve the detection and management of grounding issues in railway power networks. This article will summarize the study’s key points, discuss its significance, and analyze the advantages and limitations of online ground current monitoring.
Ground current, also known as leakage current, refers to the unintended flow of electrical current through the grounding system of a railway's power supply network. These currents can result from:
Insulation degradation in cables
Leakage faults in traction power systems
Unbalanced loads or improper grounding
Excessive ground currents can lead to safety hazards, equipment damage, and increased power losses.
Without proper monitoring, ground current issues can cause:
To address these challenges, the study proposes an online monitoring system to continuously track ground current levels in real time.
The study introduces an online ground current monitoring system based on high-precision sensors and data transmission technologies. The system consists of the following key components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Current Sensors | Detects ground leakage currents in power cables |
| Data Acquisition Module | Collects real-time electrical data |
| Wireless Transmission System | Sends monitoring data to control centers |
| Data Analysis Software | Processes and identifies abnormal trends |
| Alarm System | Triggers alerts in case of excessive ground current |
Continuous Monitoring: Sensors are installed along traction power cables to measure ground currents in real time.
Data Transmission: The collected data is wirelessly transmitted to a control center for analysis.
Automatic Analysis: Advanced algorithms process the data to detect abnormal trends.
Fault Detection & Alerts: If a leakage current exceeds a threshold, an alarm is triggered, notifying maintenance personnel.
This system allows for proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving railway network reliability.
The research demonstrates that real-time monitoring significantly improves the efficiency of ground current detection compared to traditional methods. Key findings include:
| Parameter | Traditional Monitoring | Online Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Speed | Periodic inspections (slow) | Continuous monitoring (real-time) |
| Fault Identification | Delayed detection | Instant alerts |
| Maintenance Cost | Higher due to manual checks | Lower due to automated system |
| System Reliability | Moderate | High |
| Safety Improvement | Limited | Significantly enhanced |
Result:
The study concludes that online ground current monitoring can reduce fault response time by up to 80%, allowing for faster repairs and improved railway system reliability.
Several modern railway systems worldwide are adopting online monitoring solutions for electrical safety. For example:
| Country | Railway System | Monitoring Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| Germany | Deutsche Bahn | Smart ground current sensors |
| China | High-Speed Rail | AI-based fault detection |
| USA | Amtrak Network | Wireless real-time tracking |
This demonstrates that real-time monitoring is becoming a global standard for modern railway electrification.
The online ground current monitoring system proposed in the study presents a technological advancement in railway electrification. By detecting leakage currents in real time, this system enhances safety, reliability, and operational efficiency.
AI-Powered Analysis: Future monitoring systems could use artificial intelligence to predict potential faults before they occur.
Integration with IoT: Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity could enable remote monitoring across multiple railway networks.
Cost Optimization Strategies: Advances in sensor technology may help reduce initial implementation costs.
By investing in smart monitoring technologies, railway operators can ensure safer and more efficient traction power systems, paving the way for the next generation of railway electrification.
Zhang, X., et al. "Application of Online Ground Current Monitoring in Traction Power Cable Lines."
International Railway Safety Reports, 2024.
Railway Technology Journal, Vol. 36.