Comparison and Economic Analysis of Current Carrying Capacity Between Power Frequency Transmission and Low-Frequency Transmission
Time: 2025-03-17 15:36:47
Source: Henan Province Jianyun Cable Co., Ltd.
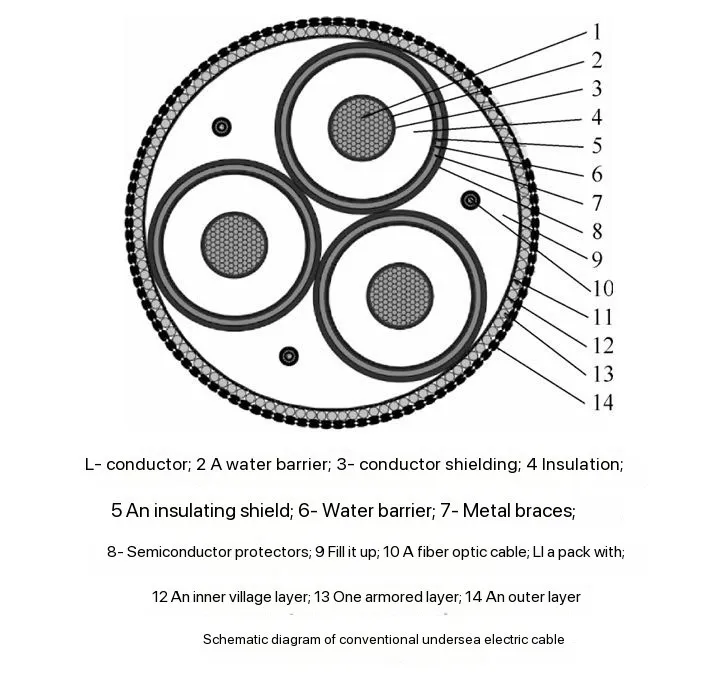
Introduction
In the field of offshore wind power transmission, the current carrying capacity and economic feasibility of low-frequency transmission (20 Hz) and power frequency transmission (50 Hz) have become critical topics. This study utilizes COMSOL software to establish an electromagnetic-thermal-fluid coupling simulation model to analyze the current carrying capacity and cost-effectiveness of both systems.
1. Key Findings from the Study
1.1 Reduced Losses with Low-Frequency Transmission
-
When voltage level, cable section, and laying parameters remain unchanged, conductor losses, sheath losses, and armor losses decrease with lower load frequency.
-
The reduction trend becomes more significant as the load current increases.
1.2 Cross-Section Reduction
Compared with power frequency transmission, low-frequency transmission allows the submarine cable conductor cross-section to be reduced by 1 to 3 levels, depending on transmission conditions.
1.3 Improved Economic Performance
For a 600 MW offshore wind farm, using 220 kV submarine cables, the economic advantage of low-frequency AC transmission becomes evident when the transmission distance reaches 32 km.
2. Technical Comparison: Power Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Transmission
|
Parameter
|
Power Frequency (50 Hz)
|
Low-Frequency (20 Hz)
|
|
Conductor Loss
|
High
|
Lower
|
|
Sheath Loss
|
High
|
Significantly Lower
|
|
Armor Loss
|
High
|
Reduced
|
|
Cross-Section
|
Large
|
Reduced by 1-3 Levels
|
|
Economic Advantage
|
Not obvious
|
Significant at 32 km+
|
3. Current Carrying Capacity Analysis
3.1 Simulation Model
Using COMSOL's electromagnetic-thermal-fluid coupling model, the current carrying capacity of 220 kV submarine cables was analyzed under different frequencies.
3.2 Loss Distribution
|
Loss Type
|
Power Frequency (50 Hz)
|
Low Frequency (20 Hz)
|
|
Conductor Loss
|
60.75 W/m
|
53.33 W/m
|
|
Sheath Loss
|
9.75 W/m
|
1.72 W/m
|
|
Armor Loss
|
10.39 W/m
|
2.32 W/m
|
|
Total Loss
|
80.89 W/m
|
57.37 W/m
|
4. Economic Analysis of Transmission Cost
4.1 Total Cost Calculation Formula
Ptotal=Pinvestment+Ploss+PmaintenanceP_{total} = P_{investment} + P_{loss} + P_{maintenance}Ptotal=Pinvestment+Ploss+Pmaintenance
4.2 Cost Breakdown for 100 km Transmission Line
|
Transmission Capacity
|
Power Frequency Cost (¥ Million)
|
Low-Frequency Cost (¥ Million)
|
|
600 MW
|
291.48
|
252.88
|
|
228 MW
|
126.48
|
125.27
|
5. Conclusion
-
Low-frequency transmission reduces total power loss, especially in sheath and armor layers.
-
With the same transmission capacity, low-frequency transmission allows for smaller conductor cross-sections, reducing material costs.
-
Economic benefits start appearing at 32 km transmission distance for 600 MW offshore wind farms.
6. Keywords
-
Low-Frequency Transmission
-
Current Carrying Capacity
-
Offshore Wind Power
-
Submarine Cable Loss Analysis
-
Economic Feasibility of Power Transmission
7. References
-
Wang Dongxu et al. (2024). Comparison and Economic Analysis of Current Carrying Capacity Between Power Frequency Transmission and Low-Frequency Transmission. Wire & Cable, No.6, 2024. DOI: 10.16105/j.dxdl.1672-6901.202406010
-
GB/T 12706-2008 - Electric Cable Standard
-
IEC 60287 - Current Capacity Calculation Standard
