Time: 2025-03-04 11:47:59 Source: Henan Province Jianyun Cable Co., Ltd.

Answer:
A solar cable is designed specifically for PV installations. These cables are engineered to handle high DC voltages, offer excellent UV and weather resistance, and maintain flexibility under varying temperature conditions. They typically feature special insulation materials that prevent degradation from sunlight and environmental exposure.
Reference: NREL and industry journals.
Answer:
The primary types include:
Answer:
Solar cables are manufactured to meet stringent industry standards such as:
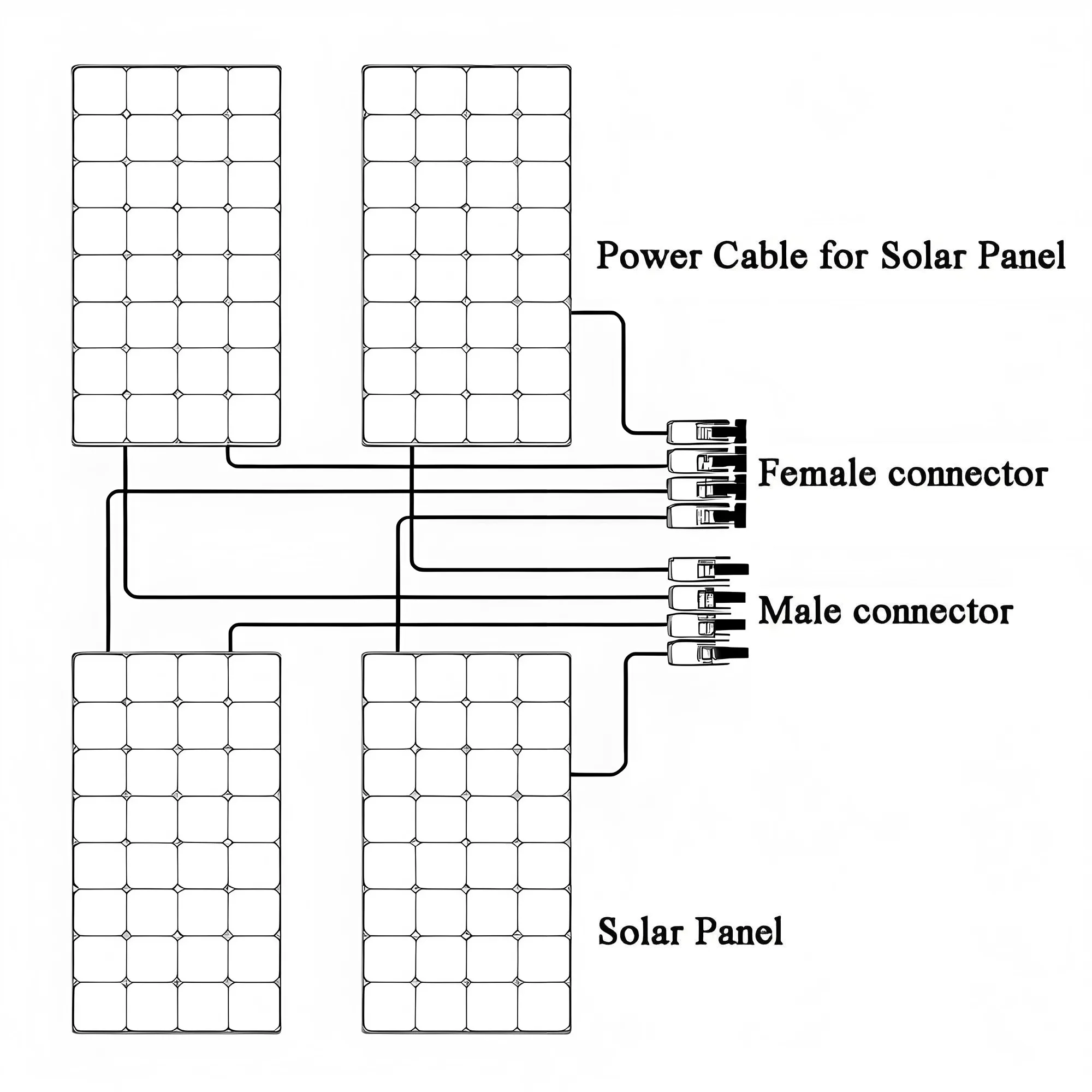
Answer:
Unlike standard building cables, solar cables are designed to resist prolonged UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, and moisture ingress. They often have thicker insulation and additional protective layers that improve durability in outdoor environments.
Reference: Industry discussions on professional forums and manufacturer guidelines.
Answer:
Key factors include:
| Cable Type | Primary Application | Key Features | Standards/Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| PV (Solar) DC Cable | DC wiring from panels to combiner/inverter | UV resistant, flexible, high DC voltage rating, designed for outdoor use | UL 4703, IEC 62930 |
| USE-2 Cable | Ground-mounted/direct burial applications | Moisture resistant, robust for direct burial, durable under outdoor conditions | UL 4703, IEC 62930 |
| AC Solar Cable | AC wiring from inverter to grid/building loads | Weatherproof, flame retardant, low smoke production, meets building codes | UL-listed for solar use |
Reference: Compiled from multiple industry sources and technical forums.

Solar cables play a critical role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of PV systems. By understanding the different types of solar cables, the relevant industry standards, and the environmental factors that affect their performance, installers and system designers can make informed decisions that lead to reliable, long-lasting solar installations.
For further reading and technical details, explore these authoritative resources: