Time: 2024-12-16 01:01:11 Source: Henan Province Jianyun Cable Co., Ltd.
Solar cables are specialized electrical cables designed for use in photovoltaic (PV) systems. These cables connect solar panels to inverters and the inverters to the grid or batteries. Their design ensures they can withstand environmental conditions and efficiently transmit the power generated by solar panels.
The key difference between solar cables and ordinary cables lies in their construction, durability, and specific use for solar power systems. Here are the main distinctions:

Solar Cables: Specifically designed for use in solar power systems. They connect solar panels to inverters, batteries, or other components in the system, transmitting DC (direct current) power.
Ordinary Cables: Used for general electrical wiring purposes in various applications, such as powering appliances, lights, and other electrical devices. These can be used for both AC (alternating current) and DC circuits.
Solar Cables: Typically made from high-quality, UV-resistant materials like cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) with an outer layer designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions like UV rays, extreme temperatures, moisture, and abrasion. This makes them durable for outdoor exposure.
Ordinary Cables: The insulation and jacket materials may not be as resistant to UV exposure, temperature extremes, or moisture, making them unsuitable for outdoor or prolonged exposure to sunlight.
Solar Cables: Designed to perform over a wider temperature range, often between -40°C to +90°C (depending on the cable type), which is crucial for solar systems exposed to varying weather conditions.
Ordinary Cables: Typically have a more limited temperature range, and may degrade or lose effectiveness when exposed to extreme temperatures or weather.

Solar Cables: They are often optimized for the specific requirements of solar energy systems, with low resistance and the ability to handle higher current levels without overheating. They are also designed to ensure minimal power loss over long distances.
Ordinary Cables: Depending on their type and purpose, these may not have the same current-handling capacity or low-loss properties as solar cables.
Solar Cables: Must comply with international standards for solar installations, such as IEC 60216, IEC 60502, and others that ensure their safety and reliability in solar power systems.
Ordinary Cables: While also adhering to electrical safety standards, ordinary cables are not built to withstand the unique challenges of solar systems, such as long-term exposure to sunlight and outdoor environmental conditions.
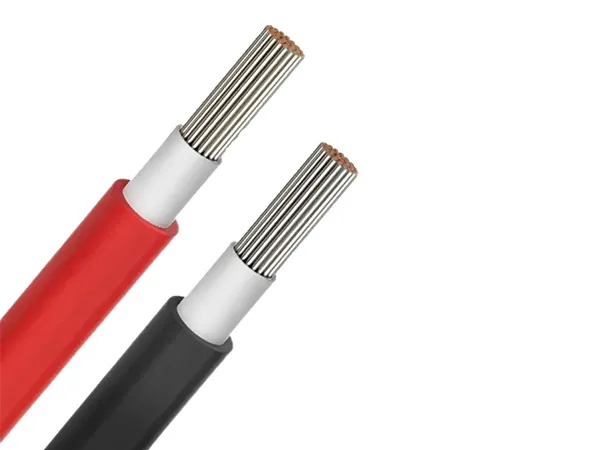
Solar Cables: Typically have distinctive color coding to indicate positive and negative conductors (usually red for positive and black for negative), which makes installation and maintenance easier.
Ordinary Cables: Also follow standard color coding (e.g., black for live wires, blue for neutral), but the color scheme may differ based on the specific application.
Solar Cables: These are designed to connect to MC4 connectors, the standard for solar panel wiring. These connectors are weatherproof and designed for secure, easy connections in solar arrays.
Ordinary Cables: Use a variety of connectors depending on the application, such as screw terminals or plug-type connectors, which are not suitable for the unique requirements of solar systems.
Solar cables are specifically engineered to endure the harsh environmental conditions typical in solar power systems, ensuring reliable and safe performance for many years. Ordinary cables, on the other hand, are more general-purpose and may not provide the same durability, UV resistance, or temperature tolerance needed for solar applications. Therefore, using the right cable for solar installations is crucial to the system's safety and efficiency.