
H03VV-F H03VVH2-F 300V Copper Round/Flat PVC Insulated PVC Sheathed Cable 3x0.75
CABLE TYPE 60227 IEC 01 THW for Thailand Myanmar Market 450/750V 70C PVC INSULAT

450/750V H07V-K Copper Wire Price 1.5mm 2.5mm Electrical Wire Copper Core Power

TUV VDE Certification 1.5mm 2.5mm 4mm 10mm 35mm Electrical Cable Wire Copper Cab
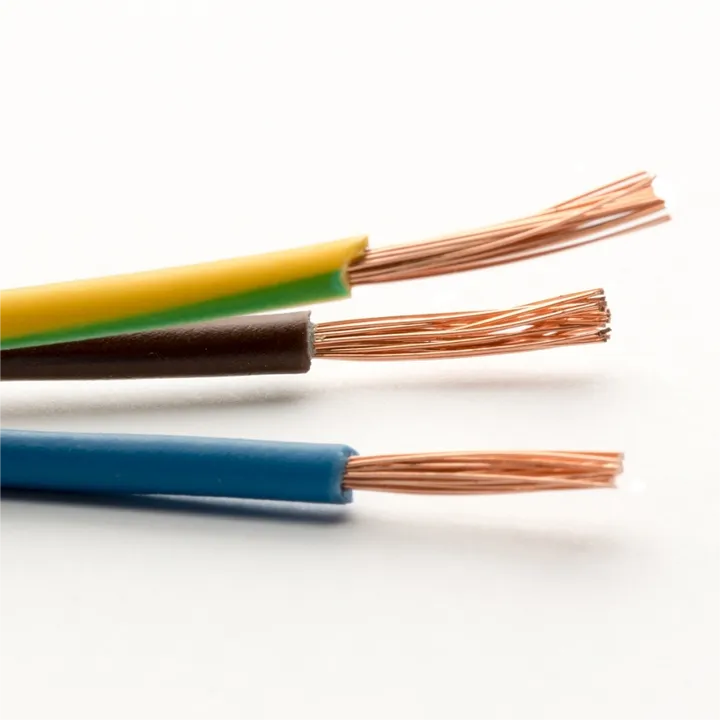
H07V-K BV 300/500V 450/750V Single Core Copper PVC Electrical Wires for House Wi
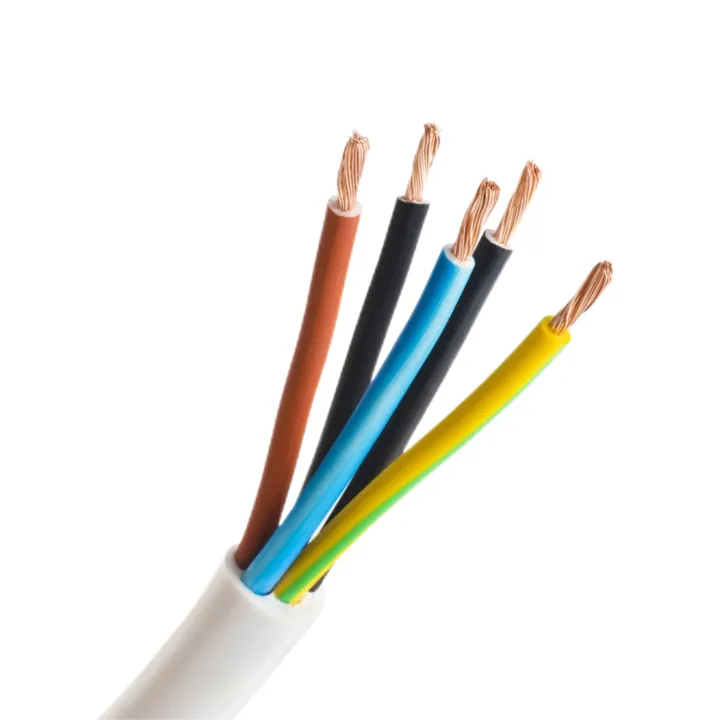

300/500V Copper PVC-insulated and Sheathed MMJ CABLE NYY CABLE NYM CABLE 3*1.5 3
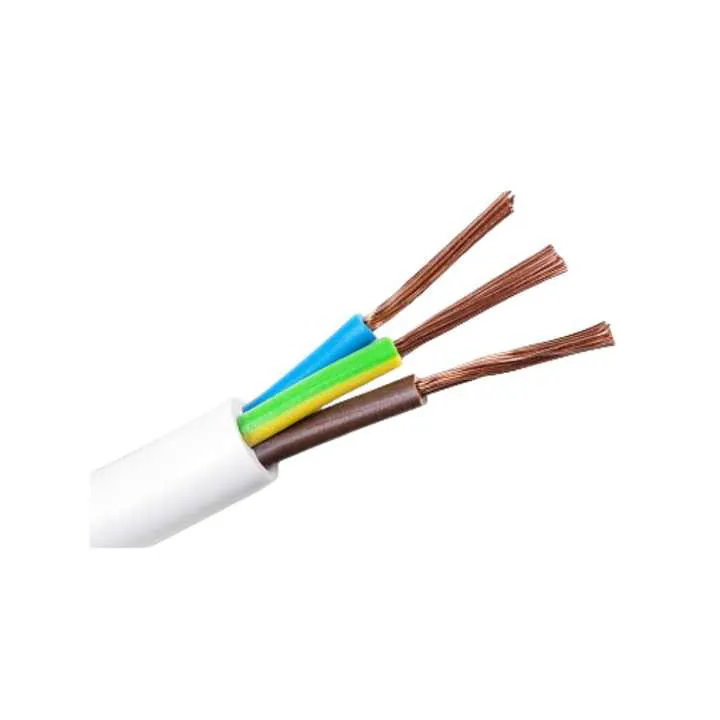

Direct Factory Price High Quality 100% 120mm Pvc Insulated Earthing Copper Cable
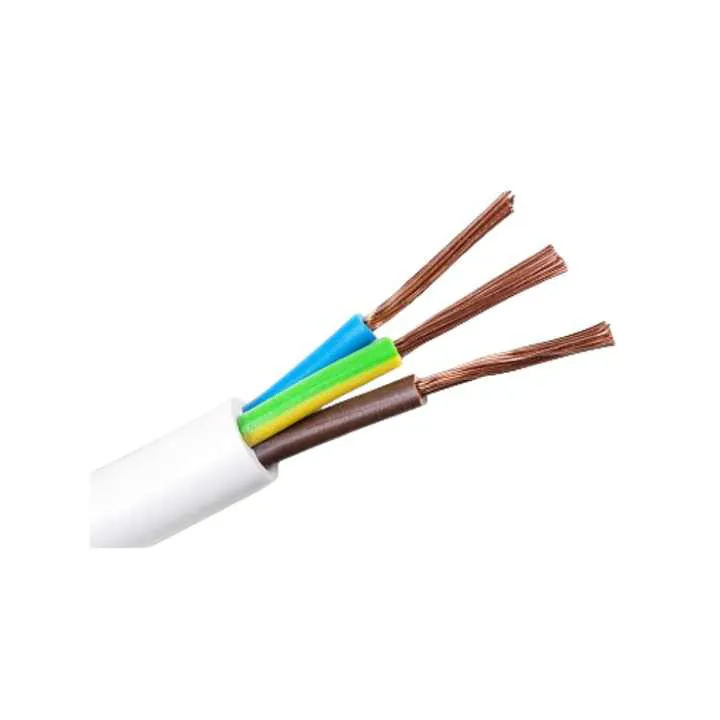

Direct Factory Price 12 Gauge Bare Copper Wire Conductor THHN Wire
Electrical wire color codes are established standards used to identify the purpose of wires within a circuit. These codes ensure safety, proper functionality, and ease of troubleshooting. The standards vary by country or region, so understanding the correct code for your area is essential.
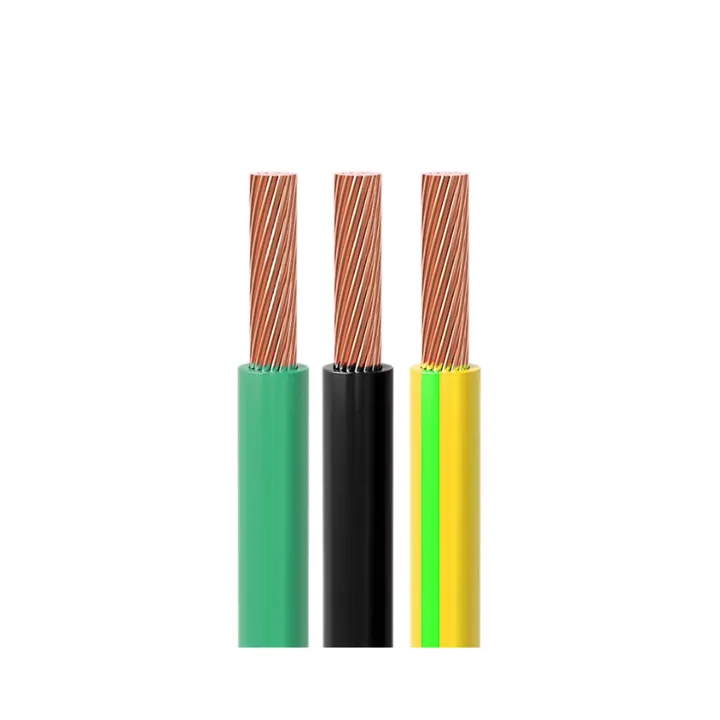
Always green or green/yellow striped.
Never used for current-carrying purposes.
Typically black, brown, or red, depending on the country and phase.
Usually blue or white.
Colors vary for phase identification, ensuring proper connection to motors or machinery.
This standard is widely adopted in Europe, Asia, and other regions following IEC 60446.
Usually consists of a single conductor (solid or stranded).
Minimal insulation layer.
Made of multiple conductors with thicker insulation.
Made of multiple conductors with thicker insulation.
Copper or aluminum for conductors.
PVC or rubber for insulation.
Made of multiple conductors with thicker insulation.
XLPE, PVC, or EPR for insulation.
Outer sheath adds mechanical protection.
Home appliances.
Internal wiring of devices.
Light-duty electrical connections.
Power distribution.
High-voltage systems.
Underground or industrial installations.